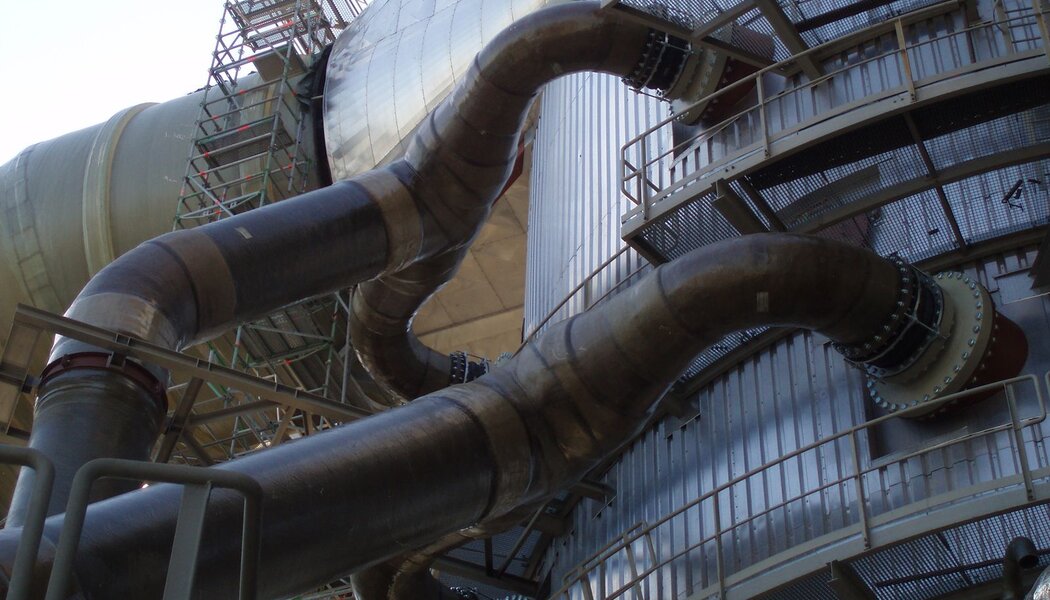
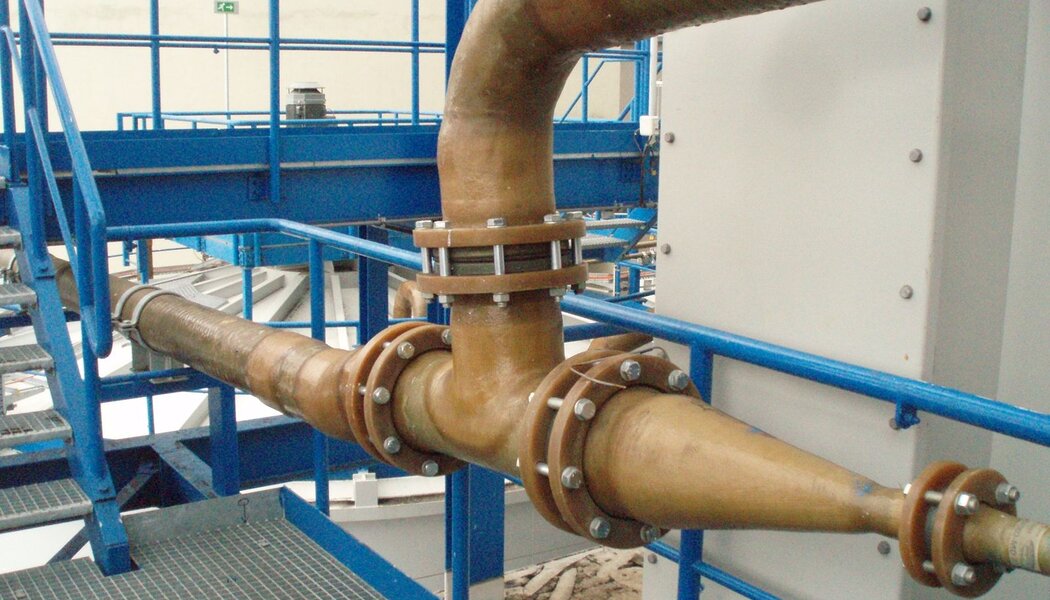
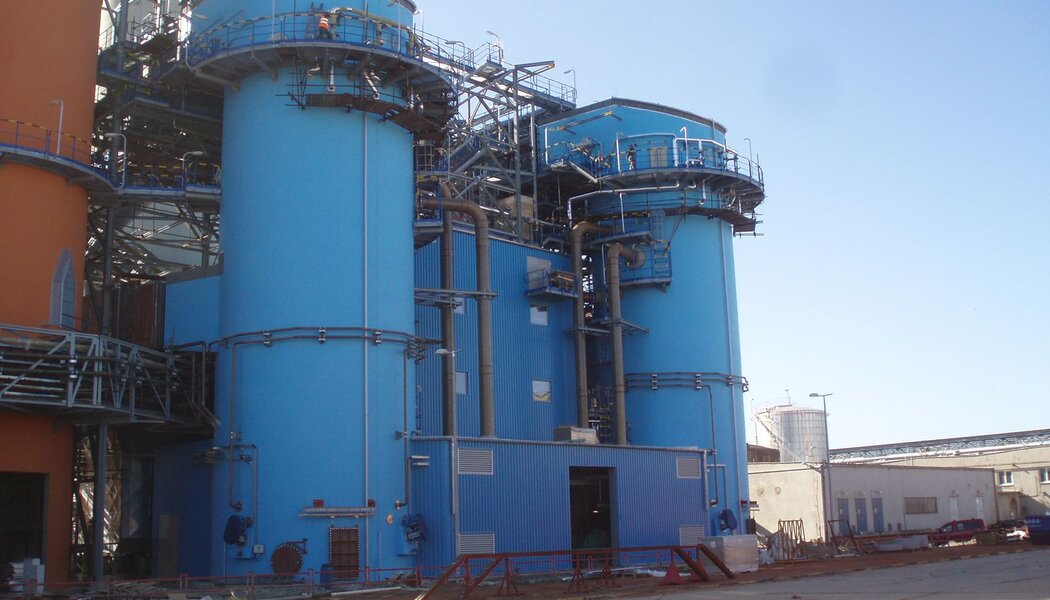
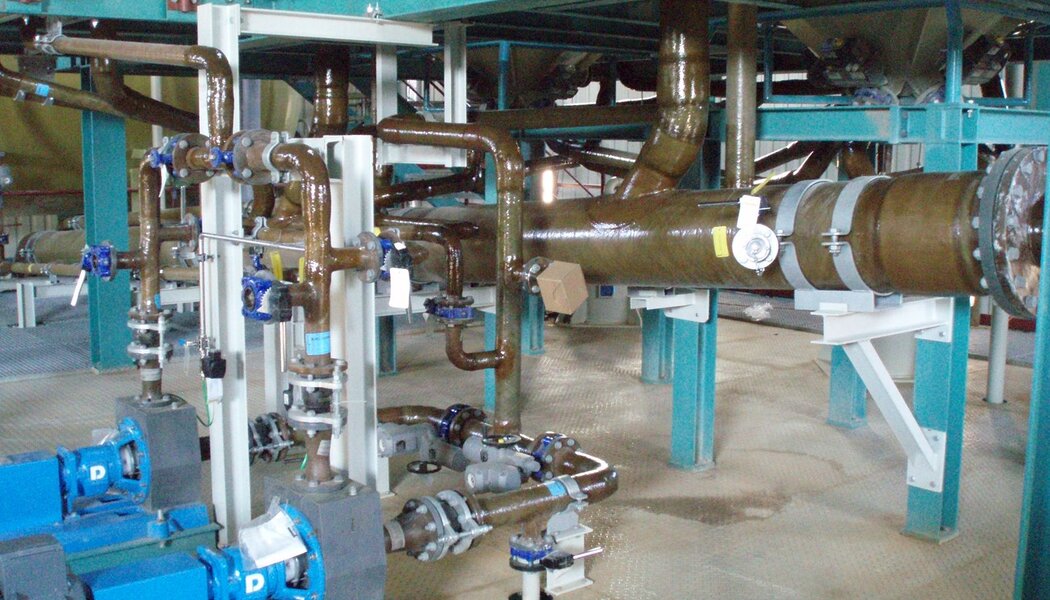
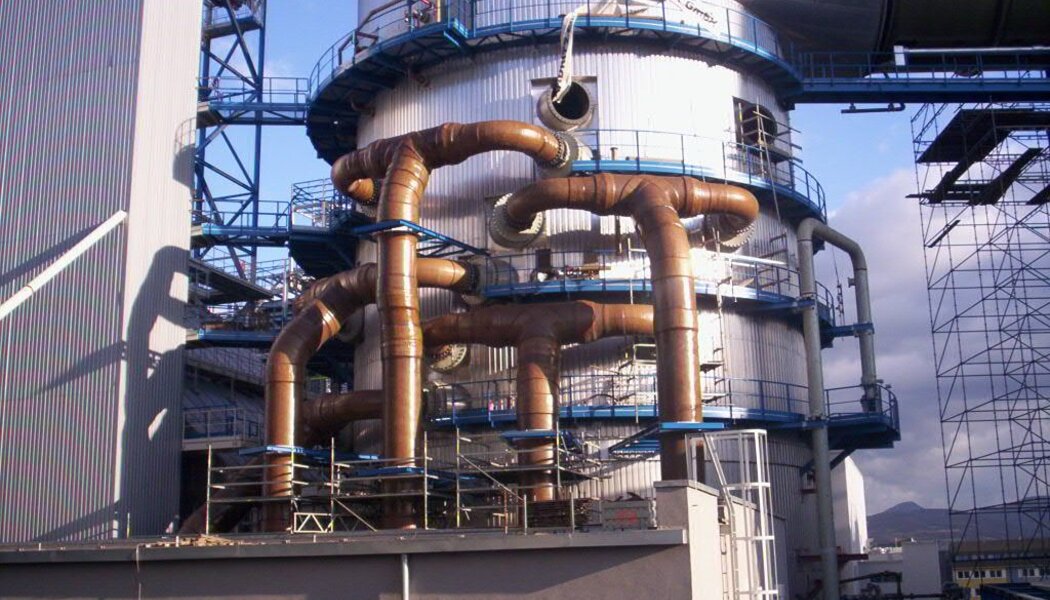
Pipes for industry and energy distribution
FRP
DN 25 - DN 4 000

up to 180 °C
custom price
Description
Chemically resistant composite pipes are machine wound from chemically resistant isophtal, bis-phenol and vinylester resins, to ensure chemical stability with a number of chemicals (acid and alcali) across a wide temperature range. The static qualities are achieved through winding a Roving mat at varying angles, which allows to simply modify static parameters both in the axial and peripheral circumferential. Depending on the application details, pipes are joined by lamination, with a glue, rubber-sealed socket joints, or flanges (fixed and loose).
| Standard technical parameters | Chemical resistance of pipes (selected examples) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | 25 - 4000 mm | Common combustion gases | up to 230 °C | ||
| PN | 1 - 16 bar | HCl (37%) | up to 80 °C | ||
| Heat resistance | up to 230 °C | H2SO4 | up to 50 °C | ||
| Hustota | approximate 1800 kg/m3 | Gas chlorine | up to 120 °C | ||
| Electric resistance | insulator as standard 1 MΩ if modified |
Water (pressurized) HCl and Cl2 vapours |
up to 140 °C up to 180 °C |
||
Ask the seller
Do you need advice on which product is right for you?
Not sure what to choose or do you have any other questions? Do not hesitate to contact us and we will be happy to help you.
Not sure what to choose or do you have any other questions? Do not hesitate to contact us and we will be happy to help you.







